Can Additive Manufacturing Replace Traditional Manufacturing?
The manufacturing realm has been revolutionized by additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing. This cutting-edge technology has captivated the imagination of many, raising the question: Can additive manufacturing replace traditional manufacturing?
For supply chain managers, additive manufacturing has undeniable advantages but is unlikely to entirely replace traditional manufacturing methods. In this article, we will explore the strengths and limitations of both approaches and discuss how they can coexist to optimize the supply chain.
The Power of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, sometimes called on-demand manufacturing, has emerged as a disruptive force, offering unique benefits that traditional manufacturing struggles to match. Its ability to create complex geometries, rapid prototyping, and customization possibilities has opened new doors for product development. By eliminating the need for specialized tooling, additive manufacturing reduces lead times and allows for on-demand production, effectively lowering inventory costs and minimizing supply chain bottlenecks. In particular, additive manufacturing is increasingly being explored as a method to remanufacture obsolete parts, including 3D printed spare parts like jigs and fixtures. Moreover, additive manufacturing reduces waste by using only the required material, making it an environmentally friendly option.

Traditional Manufacturing's Enduring Strengths
Traditional manufacturing processes have stood the test of time for good reason. They are highly efficient for large-scale production, boasting economies of scale that lower per-unit costs. Traditional manufacturing also possesses a wealth of knowledge and expertise accumulated over decades, allowing for fine-tuned processes, quality control, and high production volumes. Additionally, the ability to work with a wide range of materials and established supply chains gives traditional manufacturing a distinct advantage in certain industries, such as automotive and heavy machinery.
The Hybrid Approach: Additive and Traditional Manufacturing
Rather than an outright replacement, a hybrid approach that combines the strengths of both additive and traditional manufacturing is likely the path forward. By leveraging the benefits of additive manufacturing in the early stages of product development, companies can rapidly iterate and test designs, reducing time-to-market. Once the design is finalized, traditional manufacturing can take over to produce goods at a larger scale, maximizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
.jpeg?width=1200&height=500&name=supply-chain-digital%20(2).jpeg)
Optimizing Supply Chains With Additive Manufacturing
Integrating additive manufacturing within the supply chain can bring significant advantages. With localized 3D printing facilities, companies can reduce transportation costs and lead times, enhance flexibility, and respond quickly to market demands. This decentralized manufacturing approach also lowers the risks associated with supply chain disruptions, such as natural disasters or geopolitical events. By strategically positioning additive manufacturing facilities closer to the end users, companies can achieve faster order fulfillment, on-demand customization, and localized production, improving customer satisfaction.
Maximizing Additive Manufacturing as a Complementary Tool
While additive manufacturing holds great potential and has undoubtedly disrupted the manufacturing landscape, it is unlikely to replace traditional manufacturing entirely. The strengths of additive manufacturing lie in its ability to enable rapid prototyping, complex geometries, customization, and reduced waste. However, traditional manufacturing excels in large-scale production, economies of scale, and established supply chains.
To optimize the supply chain, a hybrid approach that combines both methods is the way forward. By leveraging additive manufacturing during the early stages of product development and integrating it strategically within the supply chain, companies can unlock benefits like reduced time-to-market, localized production, and improved customer satisfaction.
For example, analyzing part inventories for additive manufacturing use cases that shorten production lead times or reduce warehousing can demonstrate substantial value. However, few organizations have the resources or knowledge to analyze thousands of parts one-by-one.
That's where 3YOURMIND comes in.
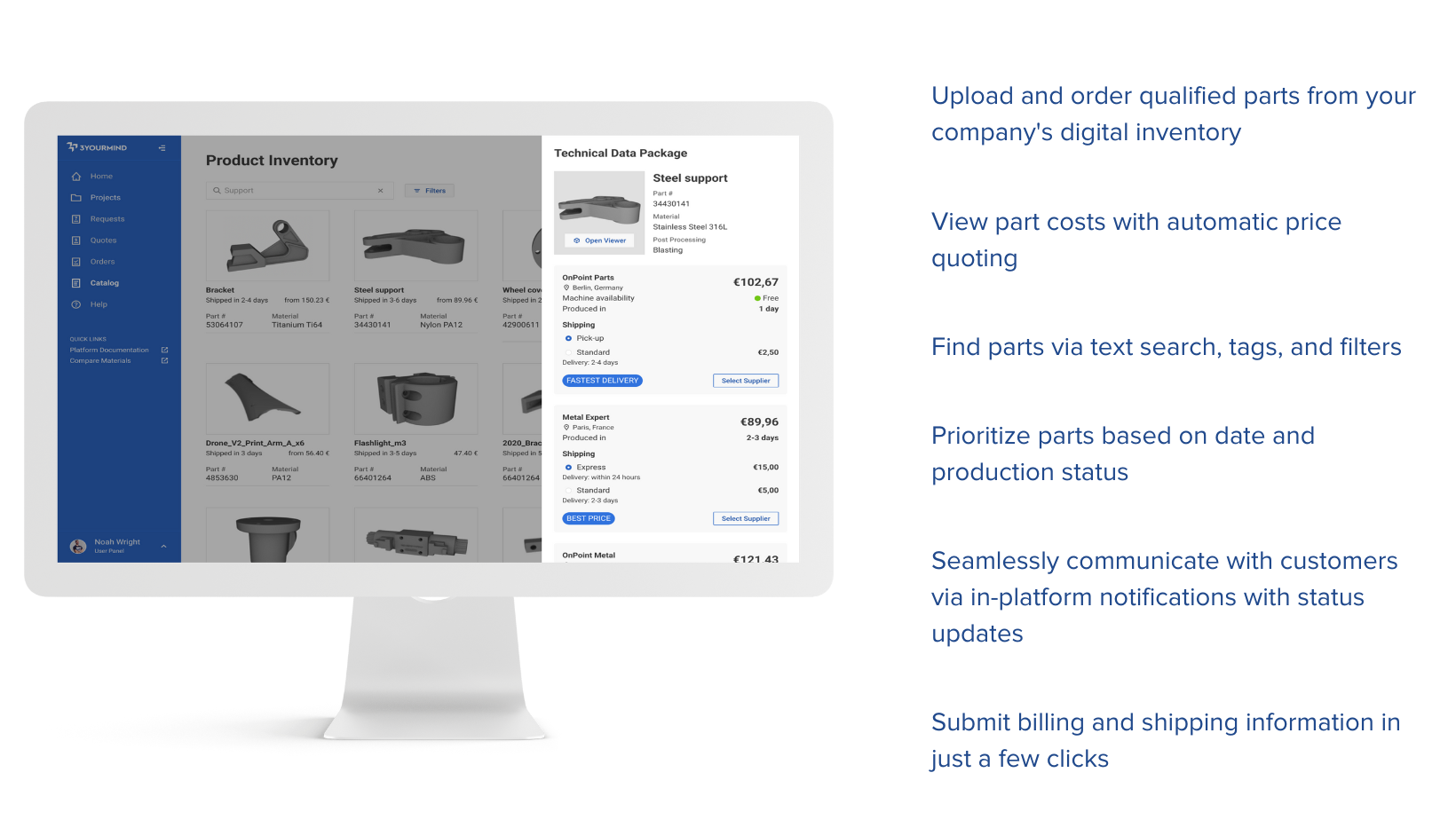
3YOURMIND offers manufacturing experts a comprehensive solution that analyzes parts, including 2D technical drawings and 3D part files, and provides a printability overview and material and technology recommendations. Once an identified part has been qualified and added to 3YOURMIND's digital inventory, supply chain managers can procure parts via their organization's in-house or distributed manufacturing facilities or through a network of approved suppliers.
Supply chain managers can instantly view price quotes and delivery timelines and communicate directly with suppliers within 3YOURMIND's centralized platform. This functionality reduces cluttered, delayed e-mail communication, ensuring approved team members can provide input, requests, or order changes in one platform to enhance collaboration. As a result, supply chain and procurement managers can ensure that their teams receive the parts they need with less red tape.
In the near future, additive manufacturing will unlikely replace serial production methods like injection molding. However, successful supply chain managers will understand the strengths and limitations of each manufacturing approach, adopting a flexible mindset that embraces the synergies between additive and traditional manufacturing to create a resilient and efficient supply chain.
Want to learn more? See how critical industries like automotive, railway, and more are successfully implementing additive manufacturing.