How to Build a Spare Parts Management Process
Struggling to get spare parts when and where you need them? Keep reading to learn how to build a spare parts management process with 3D printing.
In the fast-evolving landscape of industrial production, companies often grapple with a daunting challenge – the effective management of spare parts. As equipment and machinery age, the availability of original spare parts dwindles, exacerbated by the disappearance of manufacturers and evolving technologies.
This predicament is particularly acute for legacy systems that have been operational for decades, rendering traditional supply chains inadequate. Companies are confronted with the challenging task of ensuring uninterrupted operations while contending with prolonged lead times, exorbitant costs, and potential downtime due to the unavailability of critical components.
Because of this, strategies to address spare parts management have become imperative, propelling businesses to explore novel solutions such as 3D printing to revolutionize their approach to this intricate challenge. Using 3D printing for spare parts in your maintenance operations can offer a viable solution to mitigate the challenges you face with legacy equipment and scarce spare parts.
Here are 11 tactics to establish an effective spare parts management process using 3D printing:
11 Steps to Create a Spare Parts Management Process
1. Inventory Assessment and Prioritization:
Start by conducting a thorough assessment of your inventory. Identify critical components that are prone to failure and those that are difficult to source. Prioritize parts that are essential for equipment operation and safety.
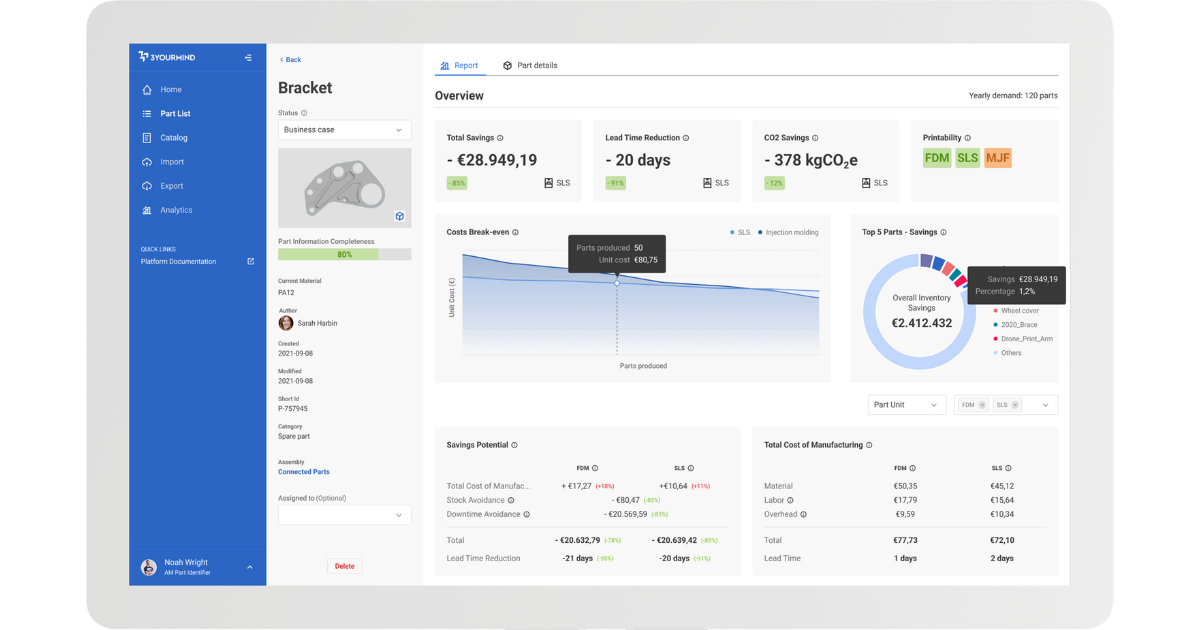
Part Screening and Business Cases evaluates parts to determine if they're economically feasible for 3D printing.
2. 3D Printing Feasibility Study:
Evaluate the feasibility of 3D printing for the identified parts. Consider factors such as material compatibility, mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and cost-saving potential. Not all parts may be suitable for 3D printing; some may be cheaper and readily available using conventional methods like CNC machining and injection molding. 3D printing shines when it can improve upon complex or legacy part designs, effectively creating a new part with less manufacturing lead time.
3. Digital Inventory and CAD Modeling:
Create a digital inventory of the parts you plan to 3D print. Develop accurate Computer-Aided Design (CAD) models for each part. These digital files will be the basis for 3D printing and can be stored in a centralized database for easy access.
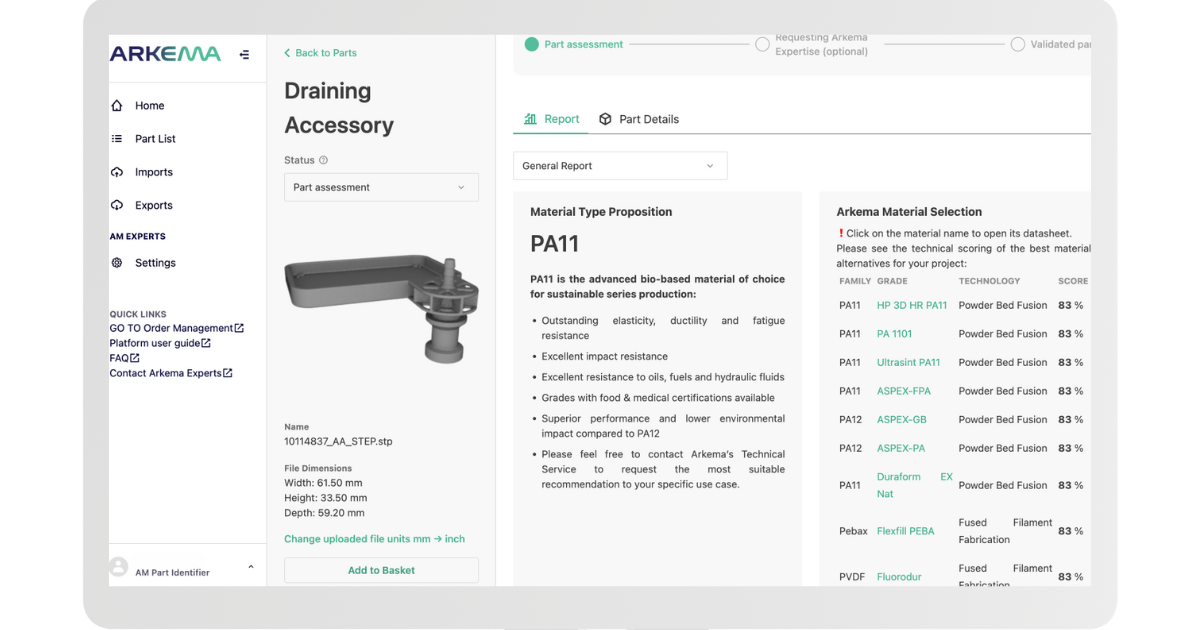
4. Material Selection:
Choose appropriate 3D printing materials that match the mechanical and environmental requirements of the spare parts. Different materials offer varying levels of strength, heat resistance, and durability. Consult with experts or conduct material testing to ensure compatibility.
5. Printer Selection and Setup:
Select the right 3D printer(s) for your needs. Consider factors such as build volume, resolution, and printing speed. Set up the printers according to the recommended specifications for the chosen materials.
6. Quality Control and Testing:
Establish a quality control process to ensure that 3D-printed parts meet the required standards. Implement testing procedures such as dimensional accuracy, mechanical stress testing, and environmental resistance assessment.
7. Documentation and Traceability:
Maintain comprehensive documentation for each 3D-printed spare part, including CAD files, printing parameters, quality test results, and installation instructions. This documentation ensures traceability and facilitates future reprints or modifications.
8. Maintenance Schedule Integration:
Integrate 3D printing into your maintenance schedule. When a part is identified as needing replacement, refer to your digital inventory to check if it can be 3D printed. If feasible, initiate the printing process and track the progress.
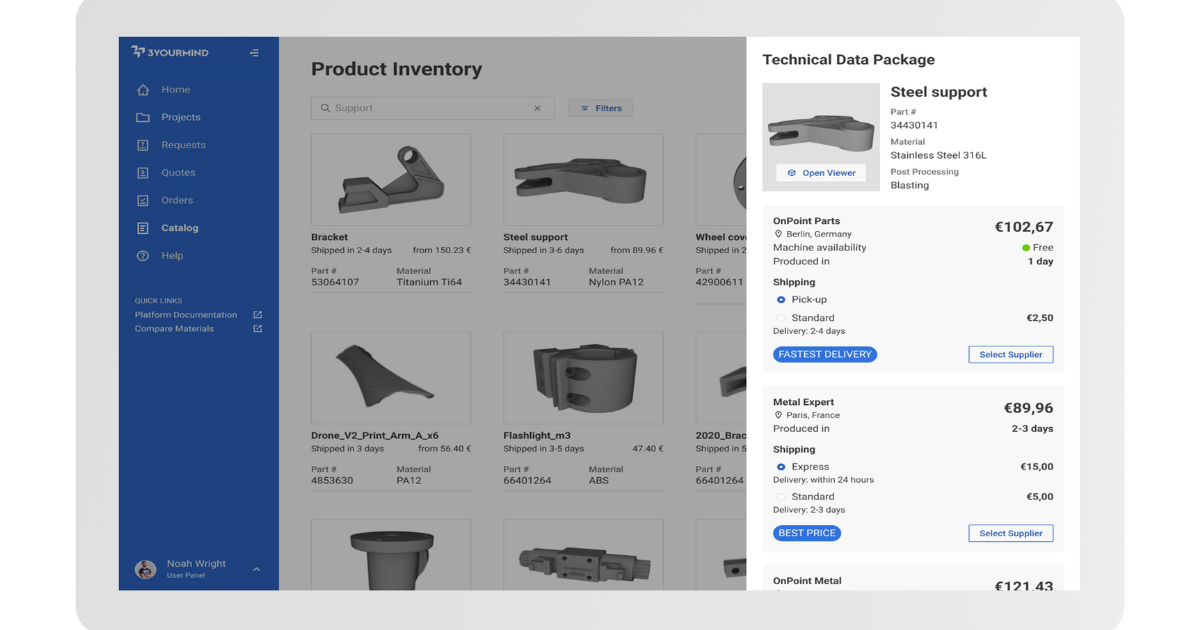 Order parts from in-house production capabilities or via approved suppliers on-demand.
Order parts from in-house production capabilities or via approved suppliers on-demand.9. Supplier Collaboration and On-Demand Printing:
Establish partnerships with 3D printing service providers or local manufacturers equipped with 3D printing capabilities. This collaboration allows you to access specialized equipment for larger or complex parts that your in-house printers may not handle.
10. Continuous Improvement:
Regularly review and improve your 3D printing spare parts process. Incorporate feedback from maintenance technicians and end-users to optimize part design, material selection, and printing parameters.
11. Training and Skill Development:
Train your maintenance team on 3D printing basics, including CAD modeling, printer operation, and post-processing techniques. Building internal expertise will enhance your team's ability to manage the 3D printing spare parts process effectively.

Additive Manufacturing: A Solution to Spare Parts Management
By implementing spare parts management process using 3D printing, you can significantly reduce lead times and supply chain dependency. Additive manufacturing lets you quickly produce custom-made components, enhancing equipment uptime and overall operational efficiency.
Remember that while 3D printing offers many benefits, it's important to approach it with a well-defined strategy and continuous improvement mindset. In this free guide, learn how organizations can reframe their approach to maintenance spare parts.

