4 Concrete Examples of Digital Manufacturing in Action
Internet of Things (IoT), key enabling technology of Industry 4.0, is defined by the ultimate connectivity between products, processes and people to improve the health of business through technology and data. This concept is highly relevant for any business entering the next decade of commercialization. By understanding the overarching strategy, tools and industry examples—it’s possible to determine how it will impact your business and operations.

Artificial intelligence and digital twins and robots, oh my! Similar to Dorothy’s trip down the yellow brick road, the next generation of industrialization is full of surprises—and Industry 4.0 may be the all-knowing, all-powerful entity that can help answer the questions and provide a path for success. However, like the Wizard of Oz, there is a lot of confusion and unknown obstacles that companies will face when adopting new practices and embracing IoT. The following article will briefly explain the overarching strategy of Industry 4.0, several tactics being used today, and the immediate impacts of those tactics to major industries. Although it seems to be a mystical concept, Industry 4.0 is simple and applicable in many ways.
Pay No Attention to the Man Behind the Curtain!
Industry 4.0 is defined by the ultimate connectivity between products, processes and people to improve the health of a business through technology and data. This concept is highly relevant for any business entering the next decade of commercialization; how for this article we will focus on B2B applications. Ultimate connectivity is heavily predicated on the use of sensors, data and artificial intelligence to streamline communication between CRM, SCM, and ERP systems. Tomorrow’s manufacturing relies on intelligent factories. Below are several tools being used today to accomplish this.
- Digitizing Assets: Major industries are adopting the digital warehouse concept and are quickly moving to a more flexible and agile way to produce or replace parts. By digitizing their assets with 3D scanning capabilities or virtually developing CAD files that represent their products, they can effectively reduce inventory and expensive overhead costs.
- Data Aggregation: Identifying, collecting and aggregating intellectual property and data is going to be an important and impactful conversation in 2021. The supply chain is going to look very different for many manufacturers due to the impetus for self resiliency. Data is the lifeblood of any production facility, and new software platforms will become the brains of the operation.
- Distributive Manufacturing: The 5 Keys to Success in a Distributed Manufacturing Model discusses the decentralization of production and the simplification of the value chain that improves efficiencies for every department. The use of additive manufacturing will directly impact the localization of products being made, which is expected to have long-lasting benefits towards sustainability for the environment and businesses.

- Continuous Improvements: The digital twin is a representation of a real-world machine, product or process that uses real-time sensory data for preemptive simulations. By quickly analyzing immediate information, the digital twin can predict machine maintenance, identify faults on the production line, and will certainly lead to a more efficient product development lifecycle. Gartner predicts that by 2021, 50% of large industrial companies will use digital twins, resulting in those organizations gaining a 10% improvement in effectiveness.
So how are these tools being used today and what industries have been influenced the most by Industry 4.0?
You’re Confusing Courage with Wisdom
Maybe the Wizard of Oz said it best; “experience is the only thing that brings knowledge.” When it comes to Industry 4.0, it’s important to carefully embrace what will work for you and your process. Throwing around terms and haphazardly investing into processes you do not understand will most likely lead to problematic results and further delay any expectation of success. What is obvious, is that data is invaluable and the competition will not wait for you.
Take a look at how some of the most influential industries are embracing Industry 4.0.
Automotive:
In May 2020, the POLYLINE Lighthouse Project was introduced, detailing BMW’s commitment to automating the production line with additive manufacturing. Research and industry is collaborating to develop a system that simplifies the manufacturing workflow, ultimately creating a lighthouse example of Industry 4.0. From CAD to 3D printing to quality assurance and production, BMW is embracing the data and setting the example. Furthermore, this level of transparency is uncommon within such a competitive industry, so we anticipate that BMW is prepared to take on a leadership role in the next generation of industrialization.
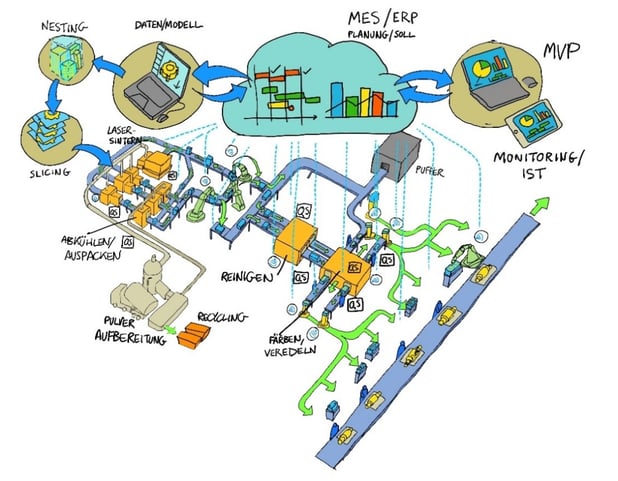 Schematic Representation of a Laser-sintering Production Line (graphics by 3YOURMIND, based on idea from G. Katsimitsoulias, Fraunhofer IML)
Schematic Representation of a Laser-sintering Production Line (graphics by 3YOURMIND, based on idea from G. Katsimitsoulias, Fraunhofer IML)
Energy:
In August 2020, 3D Printing Industry published an article about energy giant, Royal Dutch Shell announcing a four year pilot investigating digital twin technology. By embracing AR and VR platforms, Shell is able to virtually monitor real-time data from multiple sites and simplify the decision-making process from a centralized location collecting data. This commitment to Industry 4.0 is significant, and could improve critical field operations for one of the largest energy producers in the world.
Defense:
Moving from physical to digital has been a key priority for many government and defense operations across the planet. Specifically focused on becoming more agile through the use of transformational technologies that enable new business models, simplify the supply chain and reduce logistical nightmares associated with inventory and transportation. One of the goals is to embrace on-demand production with additive manufacturing that impacts FOB (Forward Operating Bases) locations across the globe. Deloitte Insights references intelligent assets in the Defense 4.0 report. This is worth a read for anyone in the aerospace or defense industry.
Transportation:
The ecosystem of energy, transportation, production and supply chain are closely tied together, and will all face new challenges for the next decade. Railroad, maritime and commercial travel will never look the same. Embracing Industry 4.0 for these particular industries requires a collection of different tactics focused on keeping their assets operational. Deutsche Bahn is actively digitizing spare parts and has integrated several key initiatives for employees and departments to move in this direction. Aggregating data to preemptively predict equipment failures and immediately producing parts with additive manufacturing is just one example of how Industry 4.0 can enhance a company’s operations and save them both time and money.
It is such an Uncomfortable Feeling to Know One is a Fool
Industry 4.0 can be a complicated subject, with tentacles expanding in many different directions. However, if your organization wants to embrace digital manufacturing then it’s imperative to investigate these tools and consider what it could mean for you. The results are still being determined, and you can either wait to see what others are doing or take incremental steps in your own operation. Ultimately, the goal of Industry 4.0 is to identify new revenue streams that improve customer service and enable innovation.
Going further...
Check out our Business Strategies to Overcome Organizational and Functional Challenges here.

